THE BERTHOLET LAB FOCUS
|
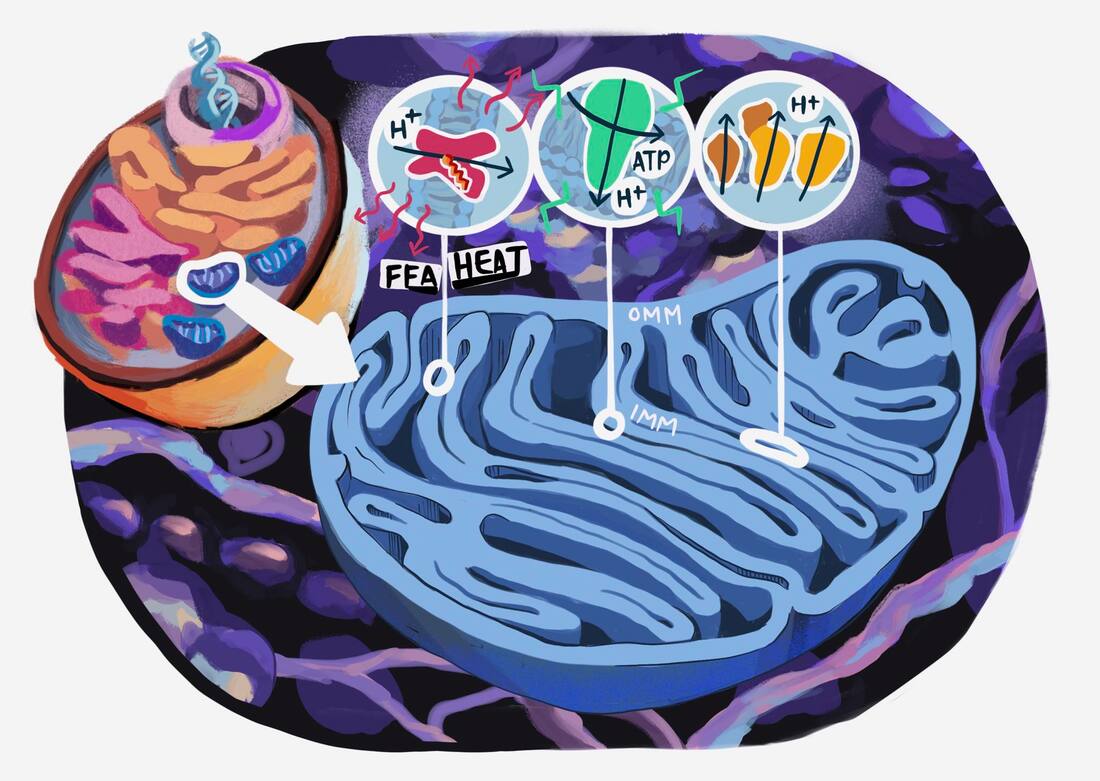
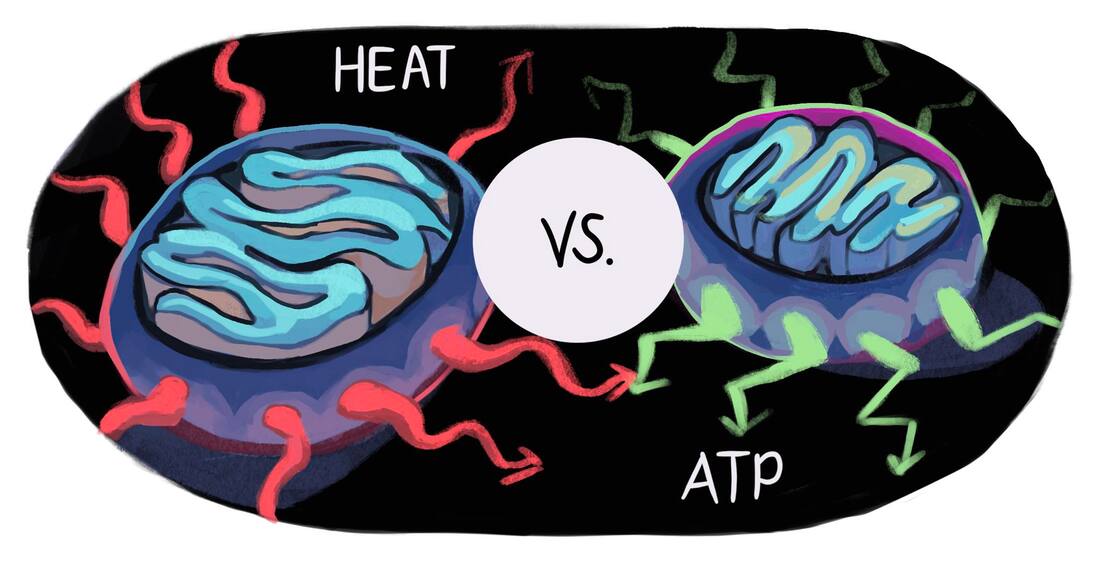
Mitochondria are organelles crucial for generating energy primarily in two ways. First, it controls cell metabolism by converting nutrients into an electrochemical gradient of protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) to generate ATP which is the energy currency of the cell. Secondly, it also converts this energy into heat, which is a process called mitochondrial thermogenesis.
Heat production also known as mitochondrial uncoupling, occurs via H+ transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane through very particular transporters called uncoupling proteins. These transporters hijack the connection between the electron transport chain activity and ATP synthase to dissipate the established H+ gradient and therefore release heat, referred to as mitochondrial thermogenesis.
|
Learn more about our research
|
Our lab will explore the mechanisms of bioenergetics using the novel mitochondrial patch-clamp assay combined with modern cellular and molecular techniques. These tools will help us grasp a fundamental understanding of how energy production and basal metabolism control physiology.
|